Okhttp3源码解析(2)-Request分析
程序员文章站
2022-10-25 17:31:10
### 前言 前面我们讲了 [Okhttp的基本用法](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8e404d9c160f) [Okhttp3源码解析(1)-OkHttpClient分析](https://www.jianshu.com/p/bf1d01b79ce7) 今天主要分析下Req ......
### 前言
前面我们讲了
[okhttp的基本用法](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8e404d9c160f)
[okhttp3源码解析(1)-okhttpclient分析](https://www.jianshu.com/p/bf1d01b79ce7)
今天主要分析下request源码!
### request初始化
当我们构建完okhttpclient对象,需要构造request对象,构造方式如下:
###### 1.get请求
```
final request request=new request.builder()
.url("https://www.wanandroid.com/navi/json")
.get()
.build();
```
###### 2.post请求
拿post提交表单请求,这时就需要声明一个requestbody对象了
```
requestbody requestbody = new formbody.builder()
.add("username", "qinzishuai")
.add("password", "123456")
.build();
request request = new request.builder()
.url("https://www.wanandroid.com/user/login")
.post(requestbody)
.build();
```
看到上面代码是不是很熟悉?和okhttpclient很相似, 没错 request 的构建也是builder模式!

我们点击request源码进去,果然 其中有静态的builder内部类:
然后我们查一下**request在初始化时配置了哪些参数???**
```
public static class builder {
httpurl url;
string method;
headers.builder headers;
requestbody body;
public builder() {
this.method = "get";
this.headers = new headers.builder();
}
//省略部分代码
public request build() {
if (url == null) throw new illegalstateexception("url == null");
return new request(this);
}
}
```
从代码看到了 如果没有声明,默认是get请求 ` this.method = "get"` ,至于`url`等字段需要我们自己去配置:
###### httpurl
请求访问的url ,可以传string与url 具体方法如下:
```
public builder url(string url) {
if (url == null) throw new nullpointerexception("url == null");
// silently replace web socket urls with http urls.
if (url.regionmatches(true, 0, "ws:", 0, 3)) {
url = "http:" + url.substring(3);
} else if (url.regionmatches(true, 0, "wss:", 0, 4)) {
url = "https:" + url.substring(4);
}
return url(httpurl.get(url));
}
public builder url(url url) {
if (url == null) throw new nullpointerexception("url == null");
return url(httpurl.get(url.tostring()));
}
```
###### method
请求类型 `string method `,支持多种请求类型
```
public builder get() {
return method("get", null);
}
public builder head() {
return method("head", null);
}
public builder post(requestbody body) {
return method("post", body);
}
public builder delete(@nullable requestbody body) {
return method("delete", body);
}
public builder delete() {
return delete(util.empty_request);
}
public builder put(requestbody body) {
return method("put", body);
}
public builder patch(requestbody body) {
return method("patch", body);
}
```
###### headers
`headers.builder ` http消息的头字段
前面看到了, **我们在初始化request的时候 同时初始化了headers**, ` this.headers = new headers.builder()`
可以通过 `header ` `addheader ` `removeheader ` ` headers ` 方法做一些操作
```
public builder header(string name, string value) {
headers.set(name, value);
return this;
}
public builder addheader(string name, string value) {
headers.add(name, value);
return this;
}
public builder removeheader(string name) {
headers.removeall(name);
return this;
}
public builder headers(headers headers) {
this.headers = headers.newbuilder();
return this;
}
```
###### body
requestbody类型,它是抽象类, 有些请求需要我们传入body实例 ,我们在通过源码来看一下:
如果是get请求,body对象传的是null
**get与head方法不能传body对象 ,其他method是可以的**
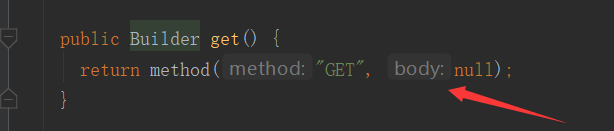
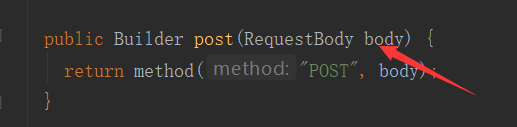
如果是post请求,就需要我们去设定了
### requestbody解析
首先我们看一下requestbody如何初始化??拿提交表单举例:
```
requestbody requestbody = new formbody.builder()
.add("username", "qinzishuai")
.add("password", "000000")
.build();
```
不出所料,也是builder模式,而且`requestbody` 是抽象类, `formbody`是`requestbody`的其中一种实现类 ,另一个实现类是`multipartbody`
requestbody源码如下:
```
public abstract class requestbody {
/** returns the content-type header for this body. */
public abstract @nullable mediatype contenttype();
/**
* returns the number of bytes that will be written to {@code sink} in a call to {@link #writeto},
* or -1 if that count is unknown.
*/
public long contentlength() throws ioexception {
return -1;
}
/** writes the content of this request to {@code sink}. */
public abstract void writeto(bufferedsink sink) throws ioexception;
/**
* returns a new request body that transmits {@code content}. if {@code contenttype} is non-null
* and lacks a charset, this will use utf-8.
*/
public static requestbody create(@nullable mediatype contenttype, string content) {
charset charset = util.utf_8;
if (contenttype != null) {
charset = contenttype.charset();
if (charset == null) {
charset = util.utf_8;
contenttype = mediatype.parse(contenttype + "; charset=utf-8");
}
}
byte[] bytes = content.getbytes(charset);
return create(contenttype, bytes);
}
/** returns a new request body that transmits {@code content}. */
public static requestbody create(
final @nullable mediatype contenttype, final bytestring content) {
return new requestbody() {
@override public @nullable mediatype contenttype() {
return contenttype;
}
@override public long contentlength() throws ioexception {
return content.size();
}
@override public void writeto(bufferedsink sink) throws ioexception {
sink.write(content);
}
};
}
/** returns a new request body that transmits {@code content}. */
public static requestbody create(final @nullable mediatype contenttype, final byte[] content) {
return create(contenttype, content, 0, content.length);
}
//省略部分代码...
}
```
核心方法有三个:
- contenttype()//数据类型
- contentlength()//数据长度
- writeto(bufferedsink sink) //写操作
今天就讲到这里,希望对大家有所帮助...
大家可以关注我的微信公众号:「秦子帅」一个有质量、有态度的公众号!

推荐阅读
-
从源码解析Python的Flask框架中request对象的用法
-
深入解析vue 源码目录及构建过程分析
-
SpringBoot 源码解析 (六)----- Spring Boot的核心能力 - 内置Servlet容器源码分析(Tomcat)
-
Tomcat源码分析三:Tomcat启动加载过程(一)的源码解析
-
从源码解析Python的Flask框架中request对象的用法
-
Mybaits 源码解析 (九)----- 全网最详细,没有之一:一级缓存和二级缓存源码分析
-
asp.net abp模块化开发之通用树2:设计思路及源码解析
-
Mybaits 源码解析 (六)----- 全网最详细:Select 语句的执行过程分析(上篇)(Mapper方法是如何调用到XML中的SQL的?)
-
Vue之Watcher源码解析(2)
-
Okhttp3源码解析(4)-拦截器与设计模式